In the fast-paced world of SaaS, innovation often takes center stage. However, neglecting security can turn a groundbreaking product into a catastrophic liability. From the initial lines of code to ongoing operations, a robust security posture is paramount. This article delves into critical security aspects – AI chat, API, and database injection – and highlights the indispensable role of Network Operations Centers (NOCs) and Security Operations Centers (SOCs) throughout the SaaS lifecycle.
The Rise of AI Chat and the Imperative of Secure Interactions
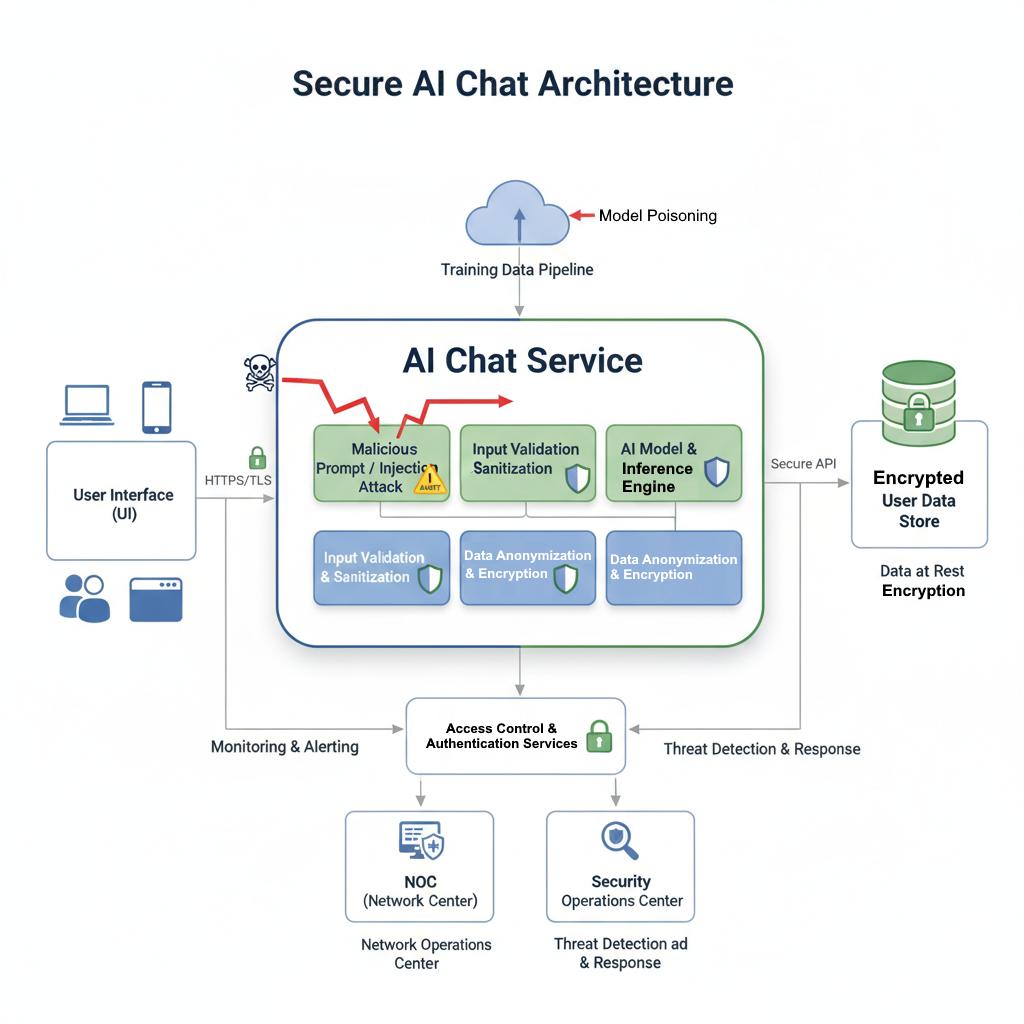
AI-powered chat interfaces are transforming customer service and user experience. But as these intelligent systems become more ubiquitous, so too do the security risks. Ensuring the security of an AI chat involves multiple layers of defense.
Data Privacy and Anonymization: AI models thrive on data. For chat applications, this often includes sensitive user information. Strict data privacy protocols, including anonymization and pseudonymization techniques, are crucial to prevent the exposure of personally identifiable information (PII). Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest.
Input Validation and Sanitization: Malicious users might attempt to inject harmful code or manipulate the AI’s responses through carefully crafted prompts. Robust input validation and sanitization mechanisms are essential to neutralize such threats. This involves checking the length, format, and content of user inputs, and stripping out any potentially dangerous characters or commands.
Model Poisoning and Evasion Attacks: Adversaries can try to “poison” the AI model during training by feeding it biased or malicious data, leading to incorrect or harmful outputs. Evasion attacks, on the other hand, aim to trick a trained model into making incorrect classifications or generating undesirable responses. Continuous monitoring of model behavior, adversarial testing, and regular model retraining with validated data are vital defenses.
Access Control and Authentication: Just like any other system, access to the AI chat’s backend infrastructure and administrative tools must be tightly controlled. Strong authentication methods, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access control (RBAC) are non-negotiable.
Diagram: Secure AI Chat Architecture
Fortifying the Gates: API Security in SaaS
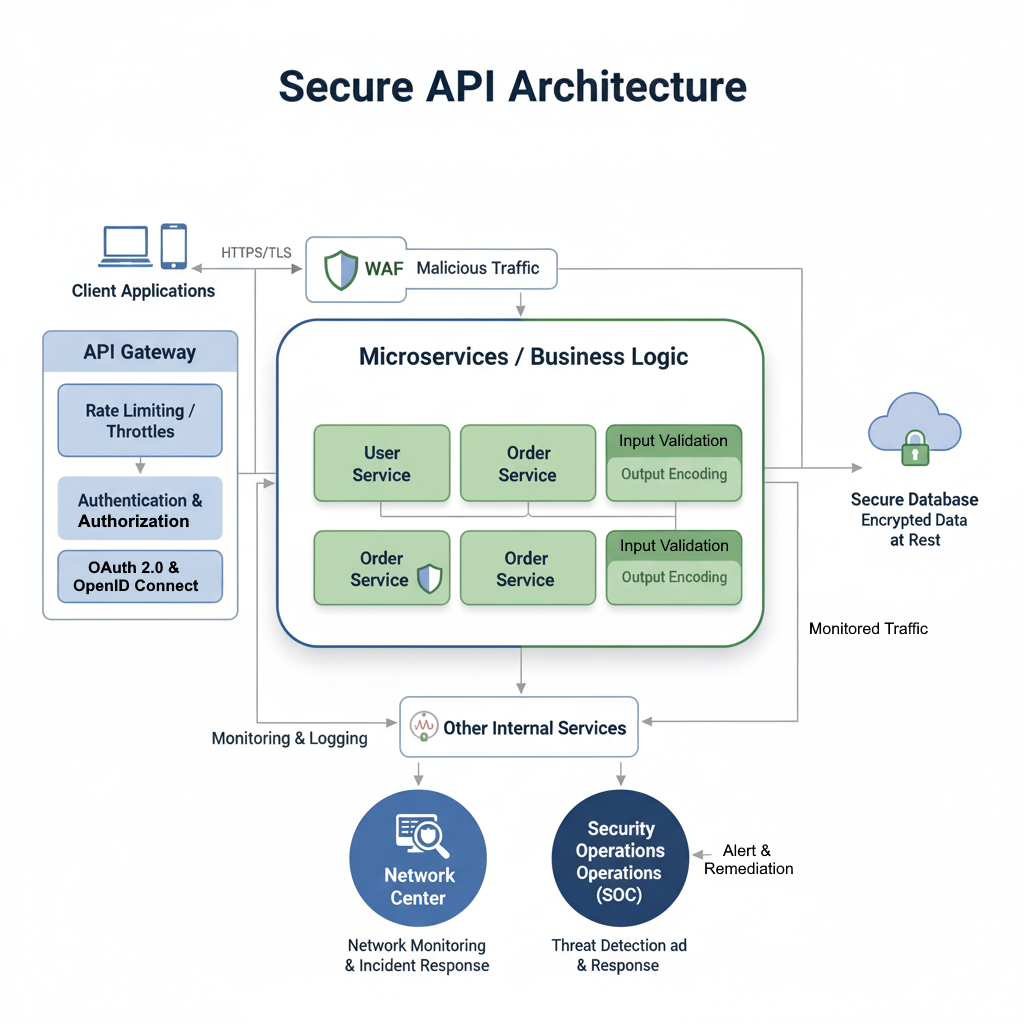
APIs are the backbone of modern SaaS applications, enabling seamless communication between different services and clients.8 However, their pervasive nature also makes them a prime target for attackers. Compromised APIs can lead to data breaches, service disruptions, and unauthorized access.
Authentication and Authorization: Every API request must be authenticated and authorized. OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect are industry standards for secure authentication flows. Authorization mechanisms, typically implemented through RBAC, ensure that users or services only have access to the resources and actions they are permitted to perform. API keys, when used, must be managed securely and rotated regularly.
Rate Limiting and Throttling: APIs can be vulnerable to Denial-of-Service (DoS) or brute-force attacks. Implementing rate limiting and throttling mechanisms helps prevent abuse by restricting the number of requests a client can make within a given timeframe.
Input Validation and Output Encoding: Similar to AI chat, all API inputs must be rigorously validated and sanitized to prevent injection attacks (e.g., SQL injection, XSS). Output encoding is equally important to ensure that data returned by the API cannot be exploited by client-side vulnerabilities.
Encryption in Transit: All API communication should be encrypted using HTTPS/TLS to protect data from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
API Gateway and WAF: An API Gateway acts as a single entry point for all API requests, allowing for centralized security policies, rate limiting, and analytics. Integrating a Web Application Firewall (WAF) provides an additional layer of defense by filtering out malicious traffic and protecting against common web vulnerabilities.
Diagram: Secure API Architecture
Protecting the Crown Jewels: Database Security and Injection Prevention
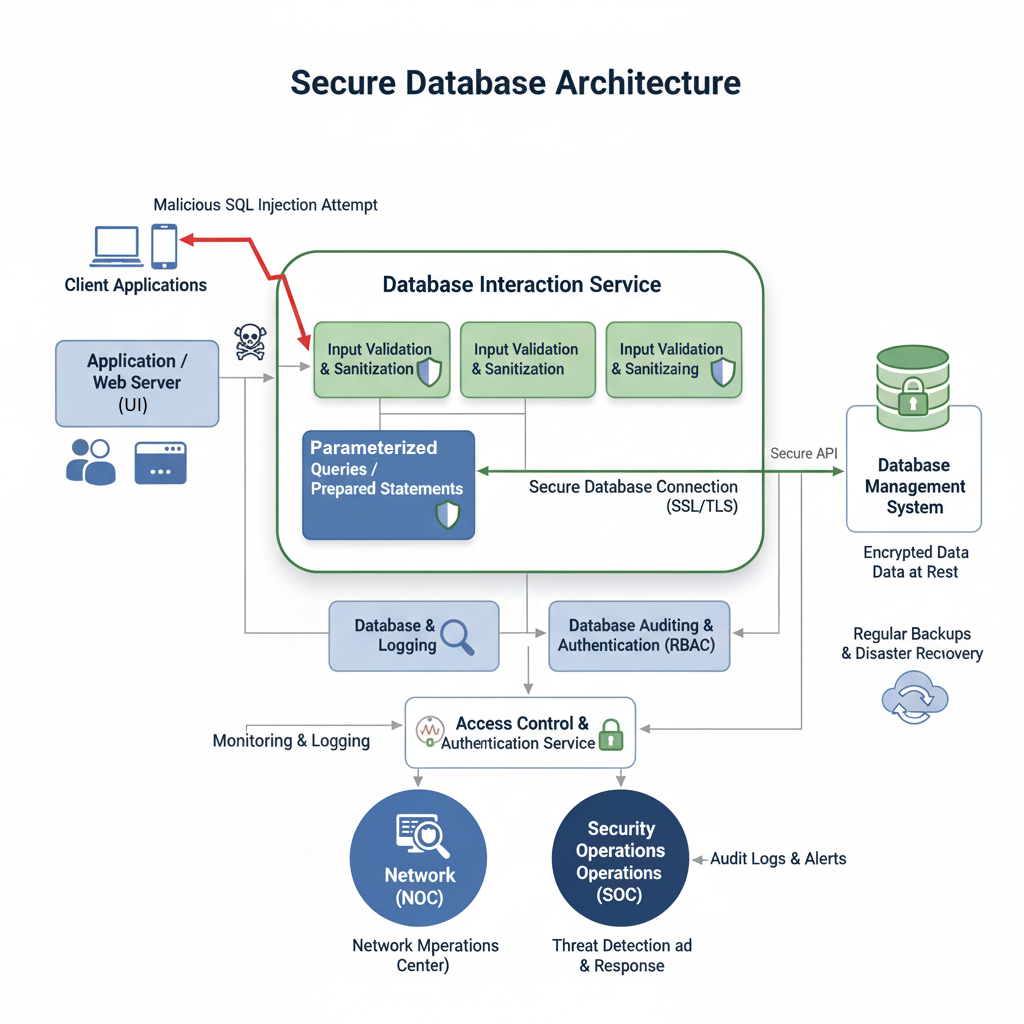
Databases are the heart of any SaaS application, storing critical user data, configurations, and business logic. A successful database breach can be devastating, leading to data loss, compliance fines, and reputational damage.
SQL Injection Prevention: SQL injection remains one of the most prevalent and dangerous web vulnerabilities. Attackers insert malicious SQL code into input fields to manipulate database queries, potentially gaining unauthorized access, modifying data, or even dropping tables.
- Parameterized Queries / Prepared Statements: This is the most effective defense against SQL injection. Instead of concatenating user input directly into SQL queries, parameterized queries separate the SQL code from the user-provided values, ensuring that the input is treated as data, not executable code.
- Input Validation and Sanitization: As mentioned earlier, validating and sanitizing all user inputs before they reach the database is a crucial first line of defense.
- Least Privilege Principle: Database users and application services should only have the minimum necessary privileges to perform their functions. Never grant root or admin privileges to application accounts.
Access Control and Authentication: Implement strong authentication for database access, including complex passwords and, where applicable, MFA. Role-based access control (RBAC) should be used to define granular permissions for different users and applications.
Encryption: Data in the database should be encrypted both at rest (using transparent data encryption or disk encryption) and in transit (using SSL/TLS for database connections).
Database Auditing and Logging: Comprehensive auditing and logging of all database activities are essential for detecting suspicious behavior, investigating incidents, and demonstrating compliance.
Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery: Implement a robust backup strategy with regular, verified backups. A well-defined disaster recovery plan is crucial to restore data and operations in the event of a breach or data loss.
Diagram: Secure Database Interactions
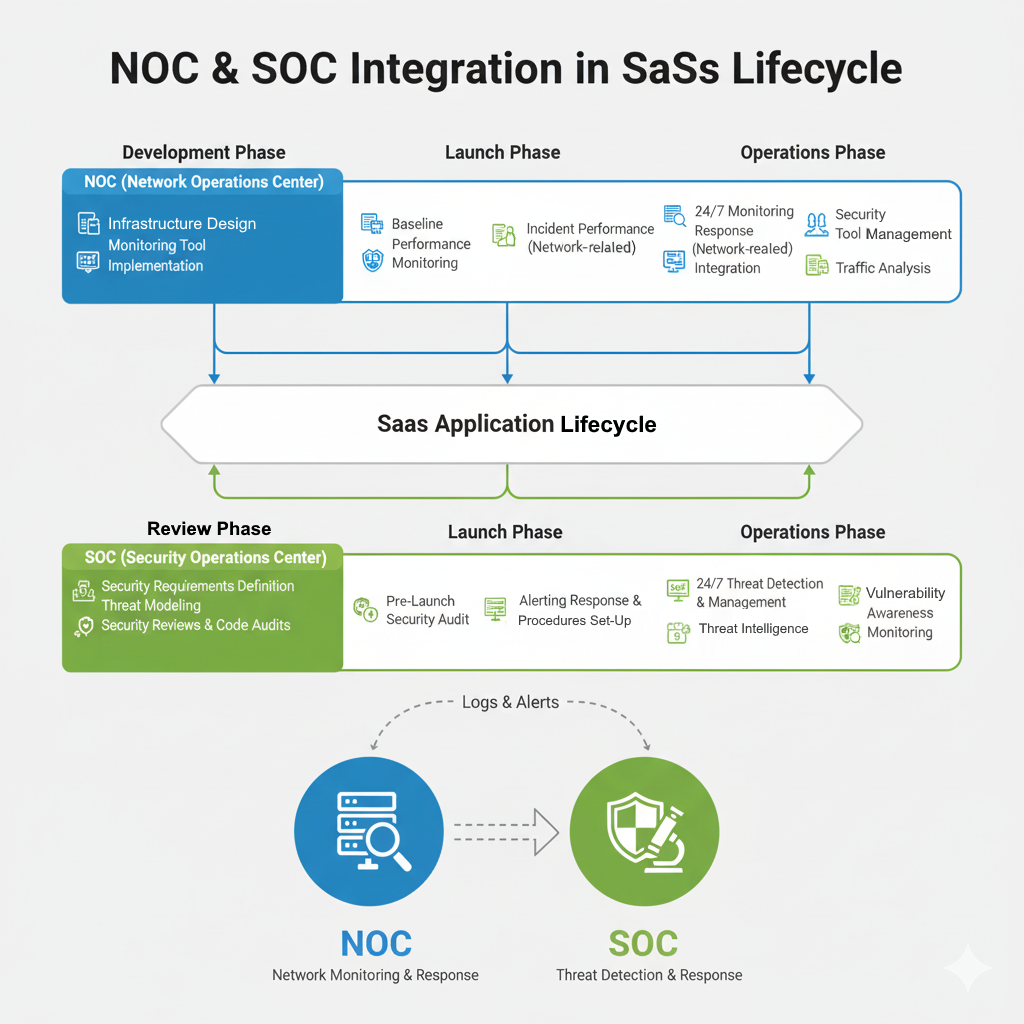
The Guardians: Role of NOC and SOC in SaaS Development and Operations
While individual security measures are vital, a holistic security strategy requires dedicated teams to monitor, detect, and respond to threats. This is where the Network Operations Center (NOC) and Security Operations Center (SOC) play an indispensable role.
Network Operations Center (NOC): Keeping the Lights On
The NOC is responsible for maintaining the availability, performance, and reliability of the SaaS infrastructure. While not solely focused on security, the NOC’s activities directly contribute to a secure environment.
Development Phase:
- Infrastructure Design Input: Providing insights on network architecture, redundancy, and scalability to build a resilient and secure foundation.
- Monitoring Tool Implementation: Setting up comprehensive monitoring tools for network performance, server health, and system uptime.
Launch Phase:
- Baseline Performance Monitoring: Establishing baselines for normal network and system behavior to identify anomalies post-launch.
- Load Testing Support: Collaborating on load testing to ensure the infrastructure can handle anticipated traffic securely.
Operations Phase:
- 24/7 Monitoring: Proactive monitoring of network devices, servers, and applications for outages, performance degradation, and unauthorized access attempts.
- Incident Response (Network-related): Responding to network outages, service disruptions, and infrastructure failures.
- Patch Management: Ensuring all network devices and operating systems are regularly patched and updated to address known vulnerabilities.
- Traffic Analysis: Identifying unusual traffic patterns that could indicate a DDoS attack or other network-level threats.
Security Operations Center (SOC): The Front Line of Cyber Defense
The SOC is the dedicated team responsible for detecting, analyzing, and responding to cybersecurity incidents. They are the ultimate guardians of the SaaS application and its data.
Development Phase:
- Security Requirements Definition: Collaborating with development teams to define security requirements and integrate security best practices into the SDLC (Secure Software Development Lifecycle).
- Threat Modeling: Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities early in the design phase.
- Security Reviews and Code Audits: Conducting static (SAST) and dynamic (DAST) application security testing, penetration testing, and vulnerability assessments.
- Security Tool Integration: Advising on and integrating security tools into the development pipeline, such as vulnerability scanners and security information and event management (SIEM) systems
Launch Phase:
- Pre-Launch Security Audit: Performing a final comprehensive security audit before the SaaS goes live.
- Establish Alerting and Response Procedures: Configuring SIEM rules and defining incident response playbooks tailored to the new application.
- Security Hardening: Ensuring all systems are securely configured according to industry best practices.
Operations Phase:
- 24/7 Threat Detection: Continuously monitoring security logs, network traffic, and system events for indicators of compromise (IOCs).
- Incident Response and Management: Investigating security alerts, containing breaches, eradicating threats, and recovering affected systems.
- Threat Intelligence: Staying updated on the latest threats, vulnerabilities, and attack techniques.
- Vulnerability Management: Regularly scanning for vulnerabilities, prioritizing remediation efforts, and tracking their resolution.
- Security Awareness Training: Providing ongoing security training for all employees to foster a security-conscious culture.
- Compliance Monitoring: Ensuring the SaaS platform adheres to relevant industry regulations and compliance standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, ISO 27001).
Diagram: NOC & SOC Integration in SaaS Lifecycle
Conclusion
In the competitive SaaS landscape, security is not an afterthought; it’s a foundational element. By meticulously securing AI chat interactions, fortifying APIs, preventing database injections, and integrating dedicated NOC and SOC teams throughout the development and operational lifecycle, SaaS providers can build an impenetrable fortress, protecting their users, their data, and their reputation. Embracing a security-first mindset from code to cloud is not just good practice – it’s essential for survival and success.






